Java-《Java语言程序设计》关于一些工具数据类型的用法总结(二) 合集collection和迭代器iterator
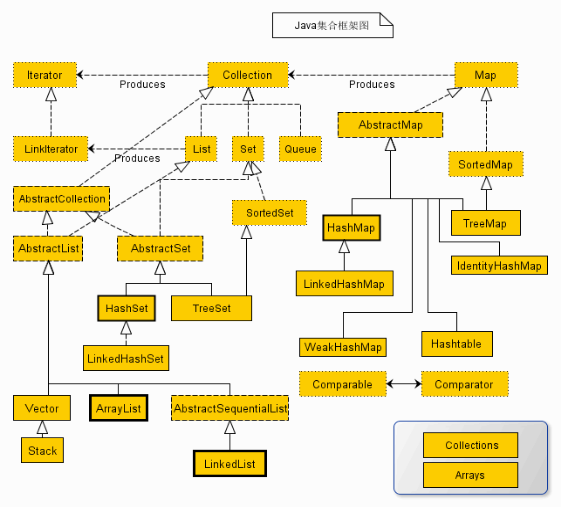
Java 合集框架(java.util.collection)支持一下两种类型的容器:
- 一种是为了存储一个元素合集,简称为合集(collection)。
- 另一种是为了存储键值对,简称为映射表(map).
合集collecion
collection 接口为线性表、向量、栈、队列、优先队列以及集合定义了共同操作。
概述
- set用于存储一组不重复的元素。
- List用于存储一个有序元素合集。
- Stack用于存储后进先出的方式处理的对象。
- Queue用于存储先进先出方式处理的对象。
- Priority Queue 用于存储按照优先级顺序处理的对象。
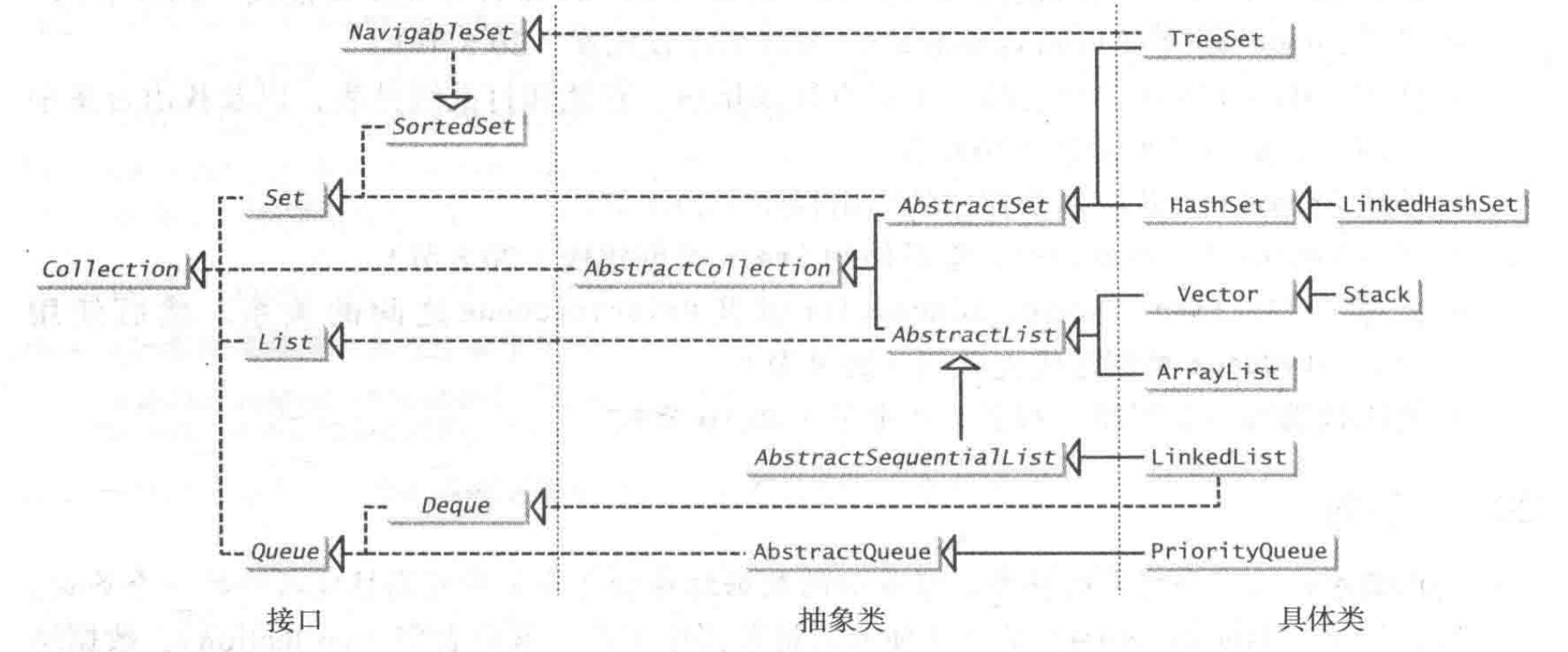
具体方法
//添加元素
add(o,E):boolean //添加一个新的元素o
addAll(c:Collection<? extends E>):boolean //将合集中的所有元素添加到该合集中
//清除所有元素
clear():void
//若包含则返回true
contains(o:object):boolean
containsAll(c:Collection<? extends E>):boolean //若合集包含C中的所有元素则返回true
//判断是否相等
equals(o: Object):boolean //若collection等于另一个则返回true
//返回哈希码
hashCode():int
//是否为空
isEmpty():boolean
//去除元素,去除则返回true
remove(o:object): boolean
removeAll(c: Collection<?>):boolean//从合集中移除C的所有元素
//保留公有元素(有点集合的味道)
retainAll(c: Collection<?>):boolean//保留同时位于C和该合集的元素
//返回合集中的元素个数
size():int
//转成数组
toArray(): Object[] //为该合集中的元素返回object数组
以下为测试代码
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> collection1 = new ArrayList<>();
collection1.add("New York");
collection1.add("Atlanta");
collection1.add("Dallas");
collection1.add("Madison");
System.out.println("A list of cities in collection1:");
System.out.println(collection1);
System.out.println("\nIs Dallas in collection1? "
+ collection1.contains("Dallas"));
collection1.remove("Dallas");
System.out.println("\n" + collection1.size() +
" cities are in collection1 now");
Collection<String> collection2 = new ArrayList<>();
collection2.add("Seattle");
collection2.add("Portland");
collection2.add("Los Angles");
collection2.add("Atlanta");
System.out.println("\nA list of cities in collection2:");
System.out.println(collection2);
ArrayList<String> c1 = (ArrayList<String>)(collection1.clone());
c1.addAll(collection2);
System.out.println("\nCities in collection1 or collection2: ");
System.out.println(c1);
c1 = (ArrayList<String>)(collection1.clone());
c1.retainAll(collection2);
System.out.print("\nCities in collection1 and collection2: ");
System.out.println(c1);
c1 = (ArrayList<String>)(collection1.clone());
c1.removeAll(collection2);
System.out.print("\nCities in collection1, but not in 2: ");
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
ietrator
Iterator 是一种经典的设计模式,用于在不需要暴露数据是如何保存在数据结构的细节的情况下,来遍历一个数据结构。Collection接口继承自Iterable接口,Iterable接口中定义了Iterator方法。
hasNext():boolean//若迭代器还要遍历更多元素则返回true
next():E //返回迭代器的下一个元素
remove():void ..移除next方法获取的上一个元素
看看示例代码
import java.util.*;
public class TestIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("New York");
collection.add("Atlanta");
collection.add("Dallas");
collection.add("Madison");
Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next().toUpperCase() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
其实可以用foreach简化
for(String element : collection)
System.out.println(element.toUpperCase() + "");
int[] 和 ArrayList转化
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = {4, 5, 3, 6, 2, 5, 1};
// int[] 转 List<Integer>
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.stream(data).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
// Arrays.stream(arr) 可以替换成IntStream.of(arr)。
// 1.使用Arrays.stream将int[]转换成IntStream。
// 2.使用IntStream中的boxed()装箱。将IntStream转换成Stream<Integer>。
// 3.使用Stream的collect(),将Stream<T>转换成List<T>,因此正是List<Integer>。
// int[] 转 Integer[]
Integer[] integers1 = Arrays.stream(data).boxed().toArray(Integer[]::new);
// 前两步同上,此时是Stream<Integer>。
// 然后使用Stream的toArray,传入IntFunction<A[]> generator。
// 这样就可以返回Integer数组。
// 不然默认是Object[]。
// List<Integer> 转 Integer[]
Integer[] integers2 = list1.toArray(new Integer[0]);
// 调用toArray。传入参数T[] a。这种用法是目前推荐的。
// List<String>转String[]也同理。
// List<Integer> 转 int[]
int[] arr1 = list1.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
// 想要转换成int[]类型,就得先转成IntStream。
// 这里就通过mapToInt()把Stream<Integer>调用Integer::valueOf来转成IntStream
// 而IntStream中默认toArray()转成int[]。
// Integer[] 转 int[]
int[] arr2 = Arrays.stream(integers1).mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
// 思路同上。先将Integer[]转成Stream<Integer>,再转成IntStream。
// Integer[] 转 List<Integer>
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(integers1);
// 最简单的方式。String[]转List<String>也同理。
// 同理
String[] strings1 = {"a", "b", "c"};
// String[] 转 List<String>
List<String> list3 = Arrays.asList(strings1);
// List<String> 转 String[]
String[] strings2 = list3.toArray(new String[0]);
}